Shared Database Container
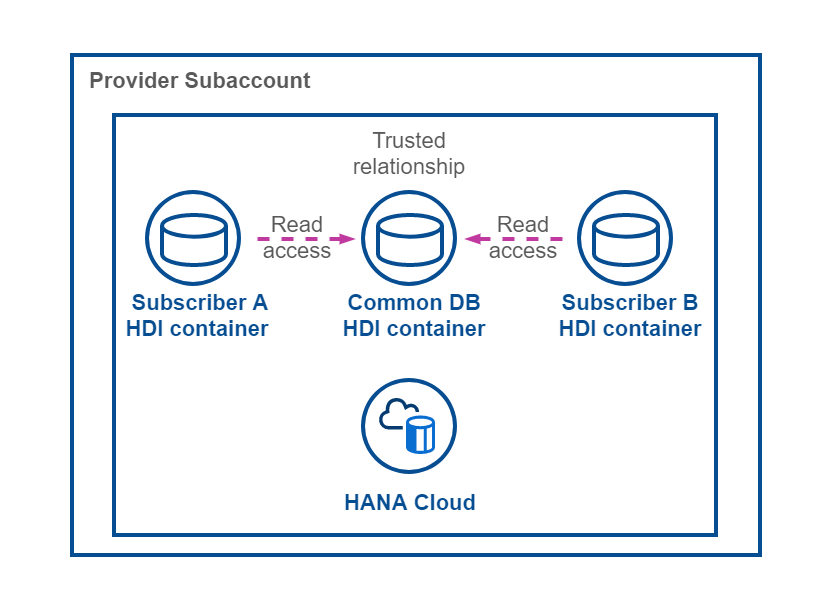
To have the ability to share data among your Consumer tenants, a shared database container is set up for this sample scenario. This allows you as a Provider to maintain e.g., master data like Languages, Countries, or Currencies in a central place and update it for all Consumer tenants.
This concept is building on the cross-container-access capabilities of SAP HANA Cloud HDI database containers. In this sample scenario, the shared database container is used to share a sample table and master data along the Tenant database containers.
1. Helm Chart definition
The HDI container required for the shared data is defined in the values.yaml file (click here) of our Umbrella Chart and created during the deployment of the SaaS application to the Provider Subaccount.
For the Tenant database container instances, SAP Service Manager (container plan) takes care of the whole container lifecycle. Therefore, there is no need to specify additional HDI resources for these containers in the values.yaml file.
# SAP HANA Cloud HDI Container
# Required for shared data model deployment
com_hdi_container:
serviceOfferingName: hana
servicePlanName: hdi-shared
To deploy content (like tables and views) to our shared database container, an additional component is required resulting in a Kubernetes Job, responsible for the deployment of your shared database artifacts.
# Shared Database Container Deployer Job
# Deploys the shared data model to a database container
hana_deployer:
image:
# Provide your HDI Container Deployer Docker Image repository
repository: <<namespace>>/susaas-db-com
tag: latest
bindings:
hana:
serviceInstanceName: com-hdi-container
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1G
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1G
To allow access from your tenant-specific database containers to the shared database container, it needs to be added as a binding to the SaaS Backend service component. This is a prerequisite as the required dependency between new Tenant database containers and the shared database container needs to be resolved upon subscription of each new Consumer Tenant.
# Backend Service Workload
srv:
port: 8080
bindings:
xsuaa:
serviceInstanceName: xsuaa
sm-container:
serviceInstanceName: sm-container
hana: # <-- Shared database container
serviceInstanceName: com-hdi-container
As you might know it from Cloud Foundry deployments, also in Kyma a so-called Service Replacement definition is required for this cross-container-access scenario. The respective environment variable is defined in the following values.yaml file (click here).
env:
SERVICE_REPLACEMENTS: '[{ "key" : "com-hdi-container", "service" : "hana" }]'
2. Tenant Database Container
The concept of cross-container-access is based on a trusted relation between containers. Still, to make the shared database container accessible from your tenant-specific database containers, some prerequisites need to be fulfilled.
The concept of cross-container-access is very powerful but not trivial. Please refer to the official documentation in SAP Help to learn more (click here).
db-com/data-model.cds
context susaas.common {
entity Shared : cuid {
value : String;
};
}
First of all, you need to assign the technical users of your Tenant containers dedicated access roles defined in the shared database container. Therefore, a role COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS is defined in the shared database container, providing READ access to a shared sample table called SUSAAS_COMMON_SHARED (see definition above). The same applies to the shared tables containing master data like Countries or Currencies. For the so-called Object Owner(s) of the accessing Tenant database containers, a similar role COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS# is required, which includes the same permissions including grant option.
db-com/src/COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS.hdbrole
{
"role": {
"name": "COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS",
"object_privileges": [
{
"name":"SUSAAS_COMMON_SHARED",
"type":"TABLE",
"privileges":[ "SELECT" ],
"privileges_with_grant_option":[]
},
{
"name":"SAP_COMMON_COUNTRIES",
"type":"TABLE",
"privileges":[ "SELECT" ],
"privileges_with_grant_option":[]
}
...
]
}
}
These roles can now be used in the Tenant database containers, where they need to be assigned to the Object Owner(s) and Application User(s) using a so-called .hdbgrants file. This file is processed before the deployment of a new Tenant database container starts. It ensures, that the technical users used during creation of new Tenant database container (but also during runtime access) have the required permissions to access the shared database container.
db/cfg/COM.hdbgrants
{
"com-hdi-container": {
"object_owner": {
"container_roles": [
"COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS#"
]
},
"application_user": {
"container_roles": [
"COM_EXTERNAL_ACCESS"
]
}
}
}
After ensuring the technical users of new Tenant database containers are assigned the required roles to access the shared database container, you need to define so-called synonyms for the shared target objects (e.g., tables or views). Therefore, two files are required. A so-called .hdbsynonymconfig and a .hdbsynonym file.
db/cfg/COM.hdbsynonymconfig
{
"SUSAAS_COMMON_SHARED": {
"target": {
"object": "SUSAAS_COMMON_SHARED",
"schema.configure": "com-hdi-container/schema"
}
},
"SAP_COMMON_COUNTRIES": {
"target": {
"object": "SAP_COMMON_COUNTRIES",
"schema.configure": "com-hdi-container/schema"
}
},
...
}
db/src/COM.hdbsynonym
{
"SUSAAS_COMMON_SHARED": {},
"SAP_COMMON_COUNTRIES": {},
...
}
Whereas the hdbsynonym file defines your synonym database object, the hdbsynonymconfig file is processed before the provisioning of a new Tenant database container and provides configuration information to the Node.js deployer. In this case, the deployer is advised to dynamically read the schema name of the shared database container from the container service details. As no fixed schema name is defined for the shared database container, the schema name is automatically generated upon deployment of the SaaS application. That's why for required references in the Tenant database containers, we need to read the schema name dynamically from the container service binding details. See it as some kind of dynamic replacement instead of providing the unique schema name which could be something like ABC123XYZ987DEF456UVW....
The synonyms can now be used in CDS model definitions or other native SAP HANA database objects like Views or Calculation Views. Just make sure to use @cds.persistence.exists annotation in case of CDS usage, to prevent the CDS compiler from creating a new database artifact for the existing synonym.
db/data-model.cds
context susaas.common {
@cds.persistence.exists
entity Shared : cuid {
value : String;
}
}
@cds.persistence.exists
extend sap.common.Countries {}
3. Keep in mind
Please keep in mind that for database container backups, cross-container access requirements cause some additional complexity. If you export a Tenant database container and plan to import it again, you first need to ensure that the technical users of the new target database container (which you're planning to import the backup in) need to have the correct shared database container roles assigned (see hdbgrants details above) before applying the backup.
The hdbgrants files will not be applied in this case and you need to assign roles manually using the HDI Container APIs of the shared database container (click here).
4. Further information
Please use the following links to find further information on the topics above:
- SAP Help - Application Router
- SAP Help - SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA Database Deployment Infrastructure Reference
- Youtube - HANA Cloud: HDI - Under the Hood
- SAP Help - Enable Access to Objects in Another HDI Container
- SAP Help - Database Synonyms in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP Help - Syntax Options in the hdbgrants File
- Youtube - SAP HANA Academy - HANACloud: Intra-HDI Container Access